SAODS – Volume 4 Issue 5
| Publisher | : | Scienticon LLC |
|---|---|---|
| Article Inpress | : | Volume 4 Issue 5 – 2021 |
| ISSN | : | 2642-1623 |
| Issue Release Date | : | May 01, 2021 |
| Frequency | : | Monthly |
| Language | : | English |
| Format | : | Online |
| Review | : | Double Blinded Peer Review |
| : | saods@scienticon.org |
Volume 4 Issue 5
Editorial
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Karimi M
In a new study, it was found that with coverage of primary molars with sealants, these teeth are less prone to caries. The researchers also found that the sealants delay the need for restorative work on these teeth. Previous researches have focused on the benefits of sealants for permanent molar teeth; unfortunately, few studies have addressed their effects on the primary teeth. The present study which was conducted by Michael Hong and his colleagues shows that their findings provide the necessary evidence to support sealants in young children.
Research Article
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Research Article
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Karol S Romero-Guamán, Kleber A Vallejo-Rosero, Andrea Gonzales-Bustamante, Viviana Chavez-Enriquez, Ivan Solani Martins, Wilber Edison Bernaola-Paredes and Frankiln R Quel-Carlosama
Introduction: Tooth extraction generates a certain level of stress and anxiety; furthermore, these factors can produce a sudden variation in blood pressure even in normotensive patients. This study aimed to determine the variation in blood pressure values and its relationship with the level of anxiety in patients undergoing dental extractions.
Methods: In total 110 adult patients, requiring simple dental extractions were selected and treated at the Surgery outpatient Clinic. Thus, the modified Corah questionnaire was applied to determine the level of anxiety and blood pressure control was performed by the auscultatory method, using a Riester © Duplex® 2.0 Stethoscope. The Riester exacta® aneroid sphygmomanometer, complying with the European standard EN1060, was used in the preoperative period, 5 minutes after the application of the local anesthetic and in the immediate postoperative period. Data were analyzed at a statistical confidence level of 95%.
Results: 98.2% (n = 108) showed a variation in blood pressure values between the pre- and postoperative time intervals, however, a significant variation occurred in the systolic pressure; the highest values were recorded in the immediate postoperative period. There was greater variability of blood pressure in patients with moderate to severe anxiety than in patients with mild anxiety. Patients from 50 – 60 years of age showed a higher variation in blood pressure values during the procedure.
Discussion: There was a significant variation in blood pressure during dental extractions in normotensive patients, and the level of anxiety shown by patients was related to the blood pressure values measured in this study.
Keywords:Arterial Pressure; Tooth Extraction; Dental Anxiety; Sphygmomanometers; Oral Surgical Procedures
Research Article
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Sukhvinder Singh Oberoi, Shabina Sachdeva, Nilima Sharma and Sunil Chaudhary
Aim and Objectives: The purpose of this study was to describe the prevalence and associated risk factors for untreated traumatic injuries of permanent anterior teeth among 11 – 14 year-old school children in New Delhi.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional survey was carried out to assess the prevalence of untreated traumatic dental injuries among 11 to 14 years old school children, attending public and private schools of New Delhi. The study recorded the type of dental trauma, size of incisal overjet, and whether lip coverage was adequate or inadequate. The relationship between traumatic dental injuries and other variables were assessed using the chi-square test and binary logistic regression analysis.
Results:The prevalence of traumatic dental injuries among 11 – 14 year school children was 10.9%. The logistic regression model showed that the age of 14 years (2.338), overjet more than 5 mm (1.685), inadequate lip coverage (1.907) and male gender (1.730) and private school (1.759) was found to be significantly associated with the traumatic dental injuries.
Conclusion: The prevalence of untreated traumatic dental injuries was found to be very high. Maxillary central incisors were the teeth most commonly affected with dental injury. Crown fracture involving enamel (Class I) was the commonly reported type of tooth injury.
Keywords:Crown Fracture; Dental Trauma; Prevalence; Tooth Injury
Case Report
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Jessica Dohoczki, José Lucas Martins, Antonio Lucio Sant’Ana Neto, Caleb Shitsuka and Irineu Gregnanin Pedron
Keywords:Crown Lengthening; Osseous Resection; Osteoplasty; Periodontal Surgery
Case Report
Volume 4 | Issue 5
Cabrera Edgar, Sabater Alejandra, Villarroel Mariana and De Santos, Erika
Cementoblastoma is a benign, slow-growing odontogenic tumor. Its most common symptoms are pain and inflammation, but the patient can be asymptomatic as well. Radiographically it can be seen as a radiopaque mass attached to the affected tooth and the recommended treatment is its extraction along with the affected tooth. This case represents a cementoblastoma located in the right mandible first molar of a symptomatic female patient where a surgery to extract both, the lion and the tooth, was performed.
Case Report
Volume 4 | Issue 5
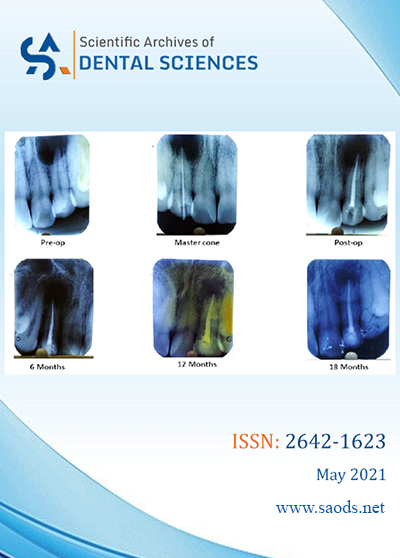
Shubhashree and Kundabala M
The present case report is 18 months follow up of conservative and successful management of a large, chronic periapical lesion in relation to maxillary lateral incisor using routine endodontic therapy. This report gives tips which are to be followed during therapy which will be helpful in healing of the lesion and long term success.
Keywords:Trauma; Nonsurgical Endodontic Approach; Periapical Lesion; Calcium Hydroxide